Setting Up OpenCode with Local Models
A completely open and free alternative to Claude Code
I was planning to take a break from the Docker Model Runner (DMR) series… and then I came across OpenCode while preparing for a DMR workshop. Naturally, I wondered — could I run OpenCode by leveraging locally hosted LLMs through DMR?
The short answer: yes!
This issue walks through setting up OpenCode with DMR. (And yes, I promise this is the last DMR issue for now 😄).
If you missed the earlier tutorials, check out my previous posts on DMR setup and model management.
Interested in building an SQL AI agent? Check out my new course on LinkedIn Learning!
Why I Started Exploring OpenCode
I’ve been using Vibe Coding heavily in recent weeks and have even shifted my team’s workflow around it. Tools like Claude Code or GitHub Copilot make AI-assisted coding incredibly productive — and the ROI at work is undeniable.
However, for personal projects, paying $100/month for a coding assistant just isn’t feasible. Once you get used to coding with AI, though, it’s tough to go back.
So, I did what we all do — turned to Google and searched “Claude Code open source alternatives.”
The top result? OpenCode.
What is OpenCode?
In short, OpenCode is an open-source AI code generation tool, similar to Claude Code. It’s a CLI tool that can connect to popular LLM APIs (like OpenAI, Anthropic, or Gemini) or any API compatible with the OpenAI SDK.
By default, OpenCode looks for common LLM API keys (e.g., OPENAI_API_KEY, ANTHROPIC_API_KEY, etc.) and automatically uses a default model.
For instance, when I first launched it, OpenCode detected my OpenAI key and connected to the GPT-5 Nano model automatically.
You can override these defaults by creating a configuration file (opencode.json) either globally or per project.
Understanding the OpenCode Configuration
By default, the OpenCode is looking for the standards LLM API keys (e.g., OpenAI, Google Gemini, Claude, etc.) and uses a default model. For example, when I first launched it, it was automatically connected to the OpenAI GPT-5 Nano model as it found my API key that was set as an environment variable (i.e., OPENAI_API_KEY). You can customize the LLM to use and other settings in the opencode config file. This file can be set at both the global and project level using the opencode.json file.
The OpenCode LLMs’ settings include the following arguments:
schema -defines the OpenCode config schemaprovider- lists the LLM API provides; You can set more than one model. This includes the following arguments:npm- the API provideroptions- the API settingsmodels- the list of LLMs (from the API provider)
Configuring OpenCode to Use DMR
OpenCode doesn’t have a built-in DMR provider, but because DMR is OpenAI-compatible, we can use the OpenAI SDK schema:
{
“$schema”: “https://opencode.ai/config.json”,
“provider”: {
“myprovider”: {
“npm”: “@ai-sdk/openai-compatible”,
“name”: “My AI ProviderDisplay Name”,
“options”: {
“baseURL”: “https://api.myprovider.com/v1”
},
“models”: {
“my-model-name”: {
“name”: “My Model Display Name”
}
}
}
}
}To make those settings work with DMR, we will have to update the DMR base URL, API key, and model settings.
In the example below, we will set the following local LLMs with DMR:
⚠️ Make sure these models are already available locally before running OpenCode.
You can pull them from Docker Hub or Hugging Face — see my earlier DMR tutorials for details.
{
“$schema”: “https://opencode.ai/config.json”,
“provider”: {
“dmr”: {
“npm”: “@ai-sdk/openai-compatible”,
“name”: “Docker Model Runner”,
“options”: {
“baseURL”: “http://localhost:12434/engines/v1”,
“apiKey”: “docker”
},
“models”: {
“ai/gpt-oss:20B-UD-Q8_K_XL”: {
“name”: “GPT-OSS:20B”
},
“ai/llama3.2:1B-Q4_0”: {
“name”: “llama3.2:1B”
},
“ai/devstral-small:24B”: {
“name”: “Devstral-Small:24B”
}
}
}
}
}We set the base URL to call the DMR server using the local host and the default TPC port. If you are using OpenCode inside a container, you should update the URL to http://model-runner.docker.internal/engines/v1.
The models section defines the models using their full tag (e.g., using ai/…), where the name argument enables setting the model name to display on the OpenCode’s model menu.
Increasing the Context Window
By default, DMR runs models with a context window of 4096 tokens. That is not sufficient for code generation tasks. Therefore, we will update the context window size from the CLI using the configure argument. For example, here is how we increase the context window size of the GPT OSS model to 100,000 tokens:
docker model configure --context-size=100000 gpt-oss:20B-UD-Q8_K_XL You should repeat this process for each model you are going to use with OpenCode.
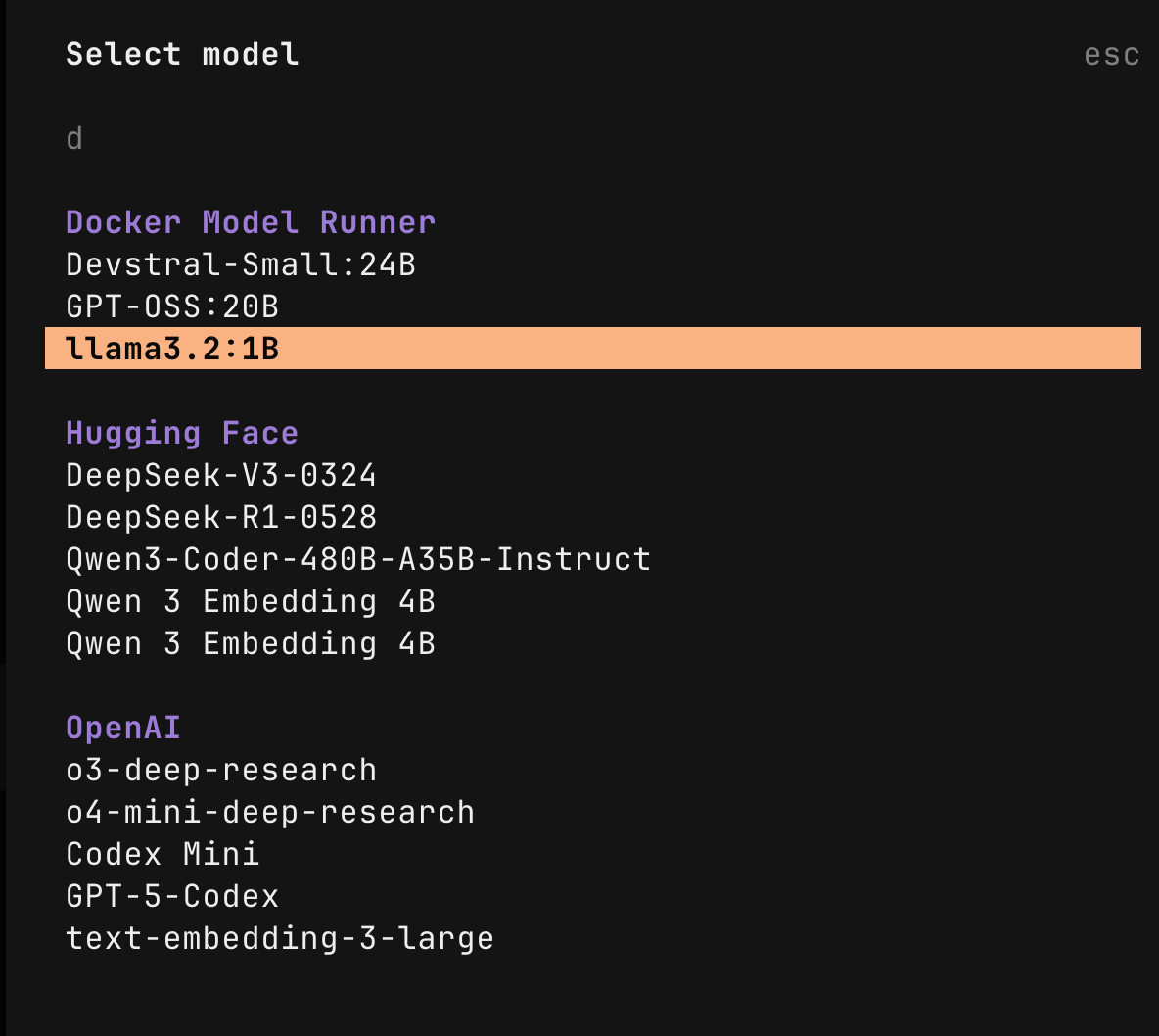
Next, launch OpenCode and use the / to pop up the menu and select models, and you should see the models you set in the models menu:
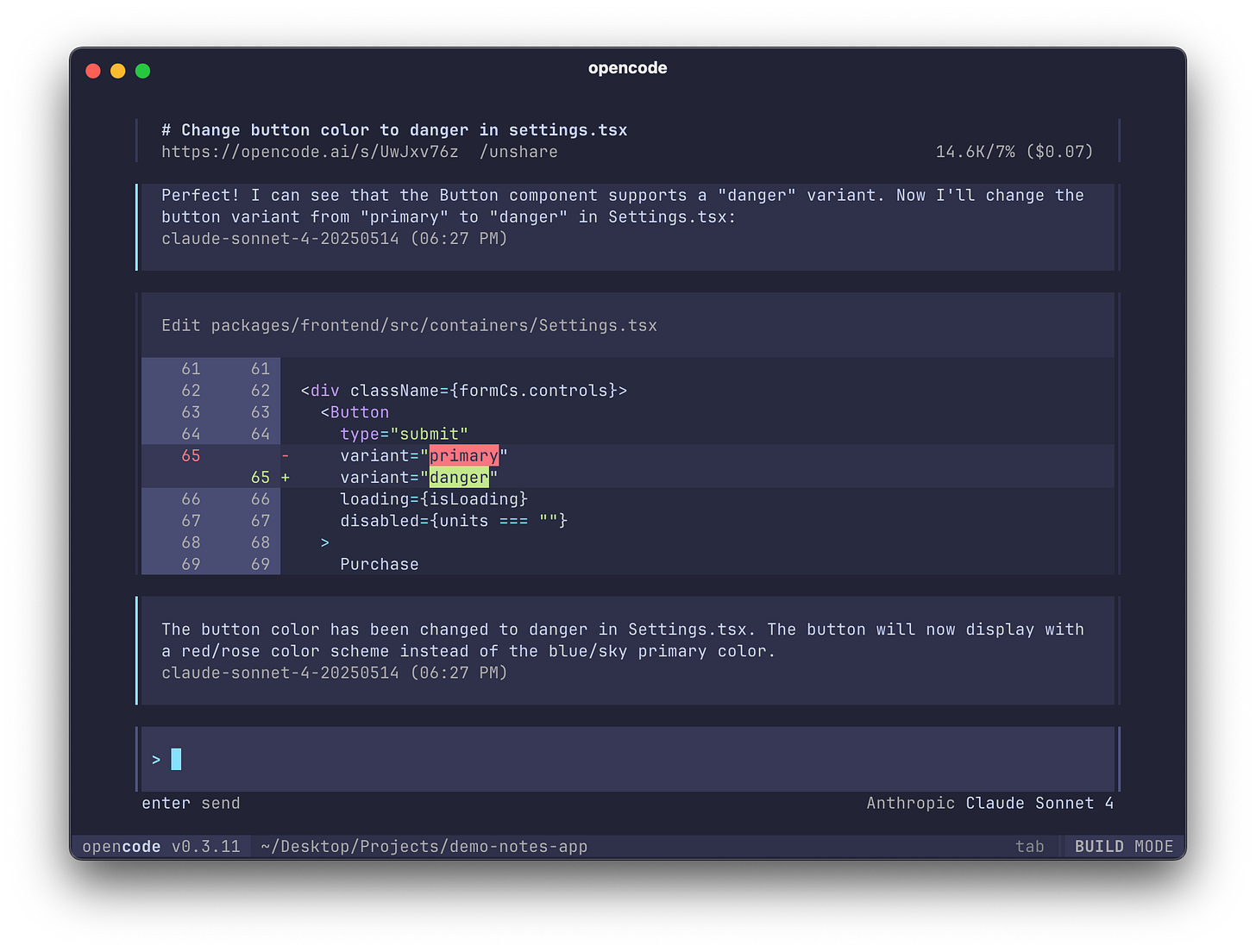
Once you select the model, you can start interacting with your local repo using the OpenCode AI agent.
Conclusions
In this tutorial, we walked through how to set up OpenCode to run LLMs locally using Docker Model Runner.
Because DMR is fully OpenAI-compatible, integration is simple and requires only minimal configuration.
Running local models gives you more privacy, control, and zero inference cost, though they might struggle with more complex code generation tasks.
A practical approach is to adopt a hybrid setup:
Use local models for lightweight or repetitive coding tasks.
Use cloud models for more advanced, long-context operations.



Thank you very much for this post! Just in case you haven’t tried it yet, you can also package the model with specific settings, such as the context window, so you don’t have to configure them every time. This also allows you to share the configured model via Docker Hub. I mention this in the following post: https://www.docker.com/blog/opencode-docker-model-runner-private-ai-coding/