Running OpenAI GPT OSS Locally with Docker Model Runner and R
This is the fourth tutorial in the Docker Model Runner sequence
In the previous issues, we reviewed how to set up Docker Model Runner, download LLMs from both Docker Hub and Hugging Face, and work with Python. This issue focuses on running the LLMs locally with R using DMR and the ellmer library. We will illustrate this workflow with the new OpenAI GPT OSS 20B model.
Tutorial level: Beginner
To get started with Docker Model Runner, check the previous issues in this sequence:
✅ Getting Started with Docker Model Runner
✅ Running LLMs Locally with Docker Model Runner and Python
✅ Docker Model Runner - Pull LLMs from Hugging Face
📌 Running LLMs Locally with Docker Model Runner and R
Let’s get started!
One of the great features of Docker Model Runner is its compatibility with the OpenAI API SDKs. On a previous issue, we saw how to use the OpenAI Python SDK to work with local LLMs using Python. To leverage this functionality in R, we will use the ellmer library, which supports a wide variety of LLM providers, particularly the OpenAI API.
The prerequisite for running DMR is Docker Engine (Linux) or Docker Desktop 4.40 and above for MacOS, and Docker Desktop 4.41 for Windows Docker Engine. For hardware requirements, please check the Docker Model Runner documentation
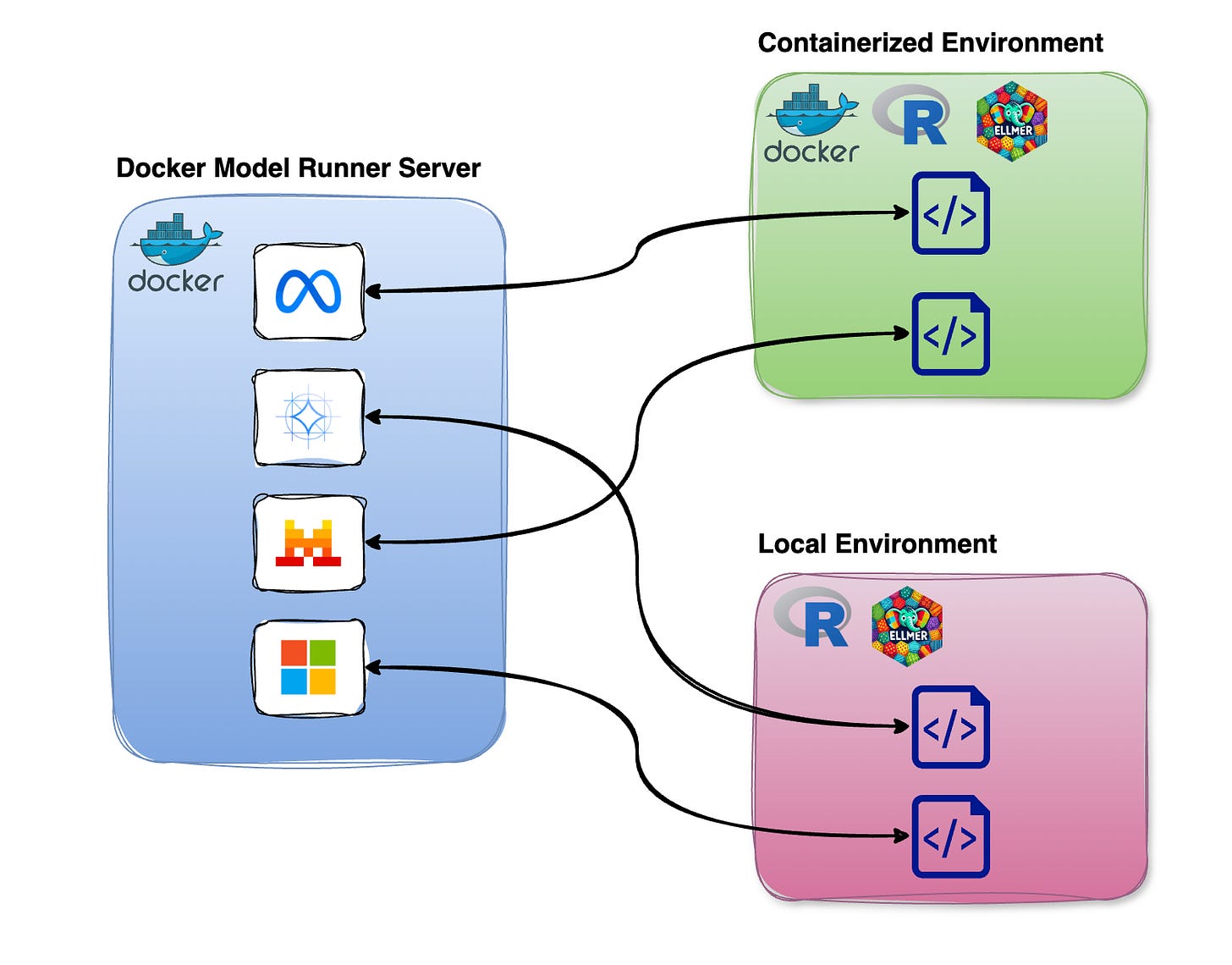
DMR runs as a standalone server, allowing you to connect to it from both containerized environments and local R setups. This provides the flexibility to call DMR from either a containerized R environment or a local R environment, as shown in the figure below.
General Workflow
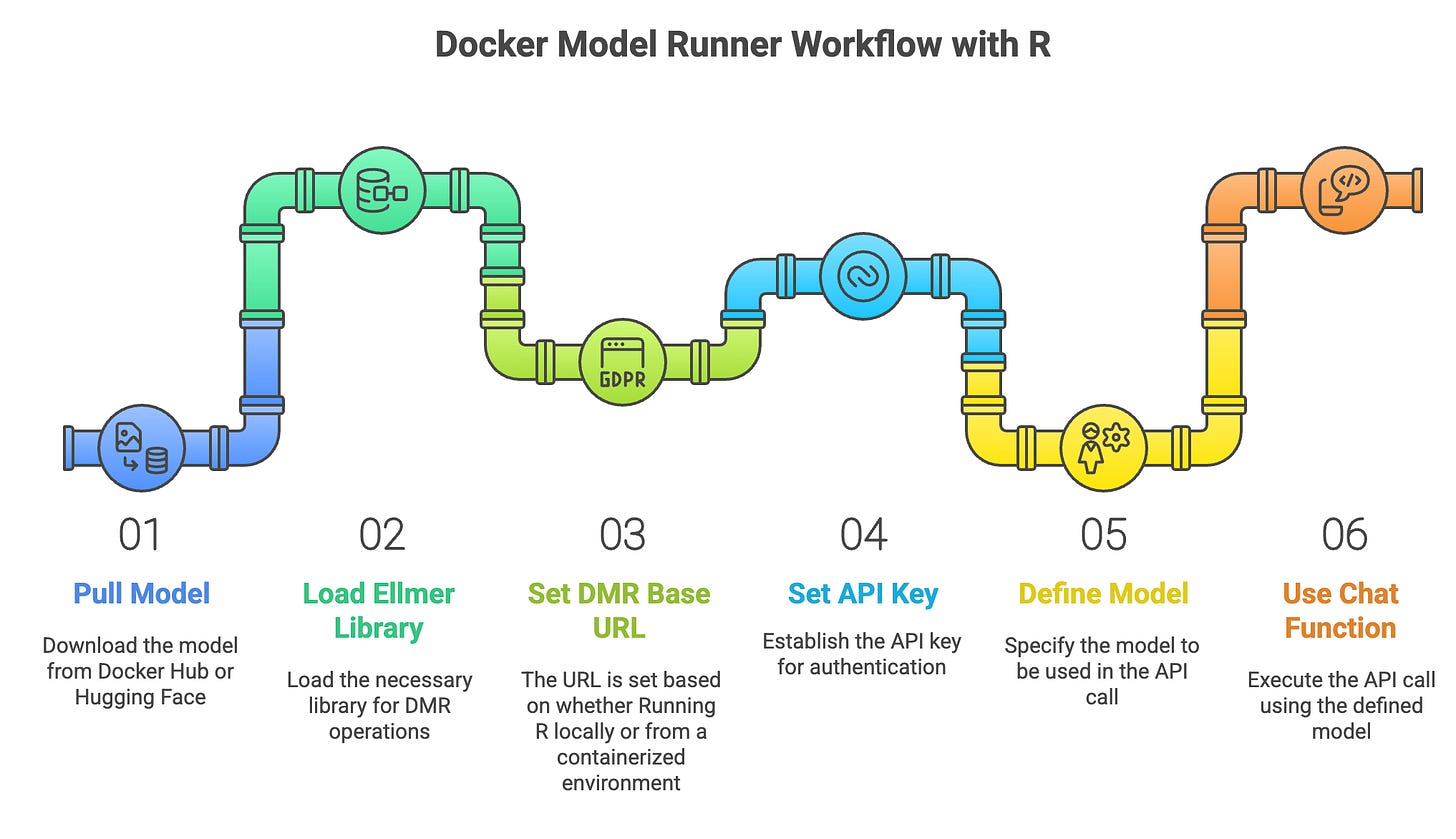
Working with DMR in R is straightforward and similar to working with the OpenAI API, following the workflow below:
Pull model from Docker Hub or Hugging Face
Load the ellmer library
Set the DMR base URL
Set the API key as “docker”
Define model
Use the
chat_openaifunction to call the model
Pulling Model from Docker Hub
Let’s start on the CLI by importing the OpenAI gpt-oss 20B model from Docker Hub using the pull command:
docker model pull ai/gpt-oss:20B-UD-Q8_K_XLNote that to pull models from Docker Hub, you need to have a Docker Hub account and authenticate from the CLI before pulling the model using the
docker logincommand. Alternatively, you can pull models using the Docker Desktop UI. A step-by-step guide is available in this issue
You can validate that the model was downloaded successfully using the list command:
docker model listThis returns a list of all models that are available locally and their details:
MODEL NAME PARAMETERS QUANTIZATION ARCHITECTURE MODEL ID CREATED SIZE
ai/llama3.2:latest 3.21 B IQ2_XXS/Q4_K_M llama 436bb282b419 4 months ago 1.87 GiB
ai/gemma3n:latest 6.87 B IQ2_XXS/Q4_K_M gemma3n 800c2ac86449 7 weeks ago 3.94 GiB
hf.co/bartowski/llama-3.2-1b-instruct-gguf 1.24B llama 7ca6390d8288 10 months ago 808M
hf.co/microsoft/bitnet-b1.58-2b-4t-gguf 2.41B bitnet-b1.58 a4b724af32b7 4 months ago 1.19B
hf.co/microsoft/phi-3-mini-4k-instruct-gguf 3.82B phi3 3e95604429e2 16 months ago 7.64B
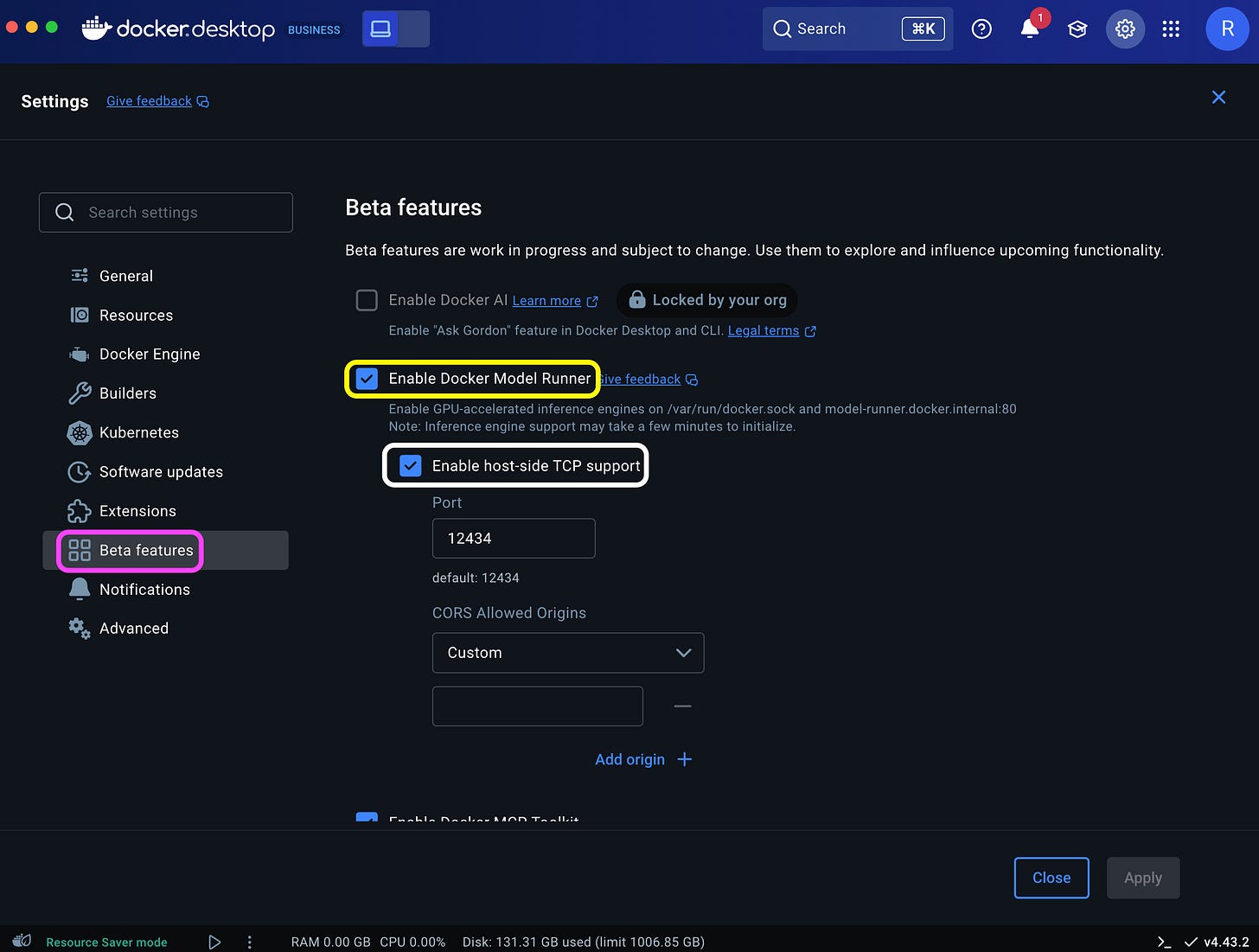
ai/gpt-oss:20B-UD-Q8_K_XL 3bdd88a27c15 8 days agoBefore connecting to the model from R, you'll need to enable the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) access and set the port number. This step defines the local host address and allows the OpenAI SDK to communicate with the DMR server.
You can enable TCP and configure the port via the Docker Desktop Settings dashboard (highlighted in white):
Or simply run the following command on the CLI:
docker desktop enable model-runner --tcp=12434This will expose the server on port 12434.
Working with LLMs with R
Now that we have a model available locally and we have defined the DMR setting, we are ready to pivot to R. Let’s load the ellmer library:
library(ellmer)Regardless of the model you are using, the DMR is compatible with the OpenAI API SDKs. Therefore, we will use the chat_openai function to interact with the DRM server, regardless of the model you are using.
Let’s define the base URL. Here, there are two options:
Using R locally (not within a container)
Using R within a container
In the first case, you should set the URL to:
base_url <- "http://localhost:12434/engines/v1"And, in the second case, you should use the following URL:
base_url <- "http://model-runner.docker.internal/engines/v1"Next, we will set the API key as “docker”:
api_key <- "docker"Last but not least, we will set the model name, in this case, using the gpt-oss model:
model <- "ai/gpt-oss:20B-UD-Q8_K_XL"Now that we have set the DMR settings, we can create a chat object using the chat_openai function:
chat <- chat_openai(
system_prompt = "You are a helpful AI assistant.",
base_url = base_url,
api_key = api_key,
model = model
)Note that we define the system prompt using the system_prompt argument. Now we can use the chat method and send a prompt:
chat$chat("What is the capital of the United States of America?")This will return the following output:
The capital of the United States of America is Washington, D.C.Summary
Using Docker Model Runner with R is straightforward, and it follows the same workflow as in Python. The DMR’s compatibility with the OpenAI API SDK simplifies and unifies the process of interacting with different LLMs by using the ellmer OpenAI API’s wrapper. This enables us to run LLMs locally and seamlessly with R.
Resources
Getting Started with Docker Model Runner - link
Docker Desktop documentation - https://docs.docker.com/desktop/
Docker Model Runner Documentation - https://docs.docker.com/ai/model-runner/
Available LLMs on Docker Hub - https://hub.docker.com/u/ai
The ellmer library - https://ellmer.tidyverse.org/index.html